600 shares are issued as floating shares to the general public, 200 are issued as restricted shares to company insiders, and 200 are kept in the company’s treasury. In this case, the company has 800 outstanding shares and 200 treasury shares. Total outstanding shares represent the number of shares of a company’s stock that are currently held by all its shareholders, including institutional investors, company insiders, and the public. The company has issued these shares, and are in the hands of investors who may buy and sell them on the open market. The issuance of common stock cannot be more than the authorized number but can give less than the number of authorized shares. So, in this case, the https://www.instagram.com/bookstime_inc number of shares issued is equal to the company’s outstanding shares.
- The number of treasury shares held by companies is reported in the treasury stock account.
- While outstanding shares are a determinant of a stock’s liquidity, the latter is largely dependent on its share float.
- Specifically, the number of actual shares outstanding must be altered to what it would have been if the split or dividend had occurred at the year’s start.
- The market cap is calculated by multiplying the current market price per share by the total number of outstanding shares.
- How much of the business your one share buys depends on the total common stock outstanding, a figure you can easily determine using the company’s balance sheet.
What common stock outstanding means

Obviously, those option holders in theory could exercise their options to create new shares. Should they do so, however, they would also contribute $50 million in cash to the corporate treasury. By issuing securities or reducing ownership stakes, the money was obtained. On the other hand, the transaction’s credit impact is reflected in the equity balance. Generally speaking, stocks with smaller floats will https://www.bookstime.com/ experience more volatility than those with larger floats.
- By comparing total equity to total assets belonging to a company, the shareholders equity ratio is thus a measure of the proportion of a company’s asset base financed via equity.
- Generally speaking, stocks with smaller floats will experience more volatility than those with larger floats.
- Many companies buy back shares as part of their capital allocation strategy.
- Next, you’ll want to look for the common stock line item on the company’s balance sheet.
- Often, a company does this to meet listing requirements, which often require a minimum share price.
- Restricted stock are shares that are owned by company insiders, employees and key shareholders that are under temporary restriction, and therefore cannot be traded.
Calculating Basic Shares Outstanding
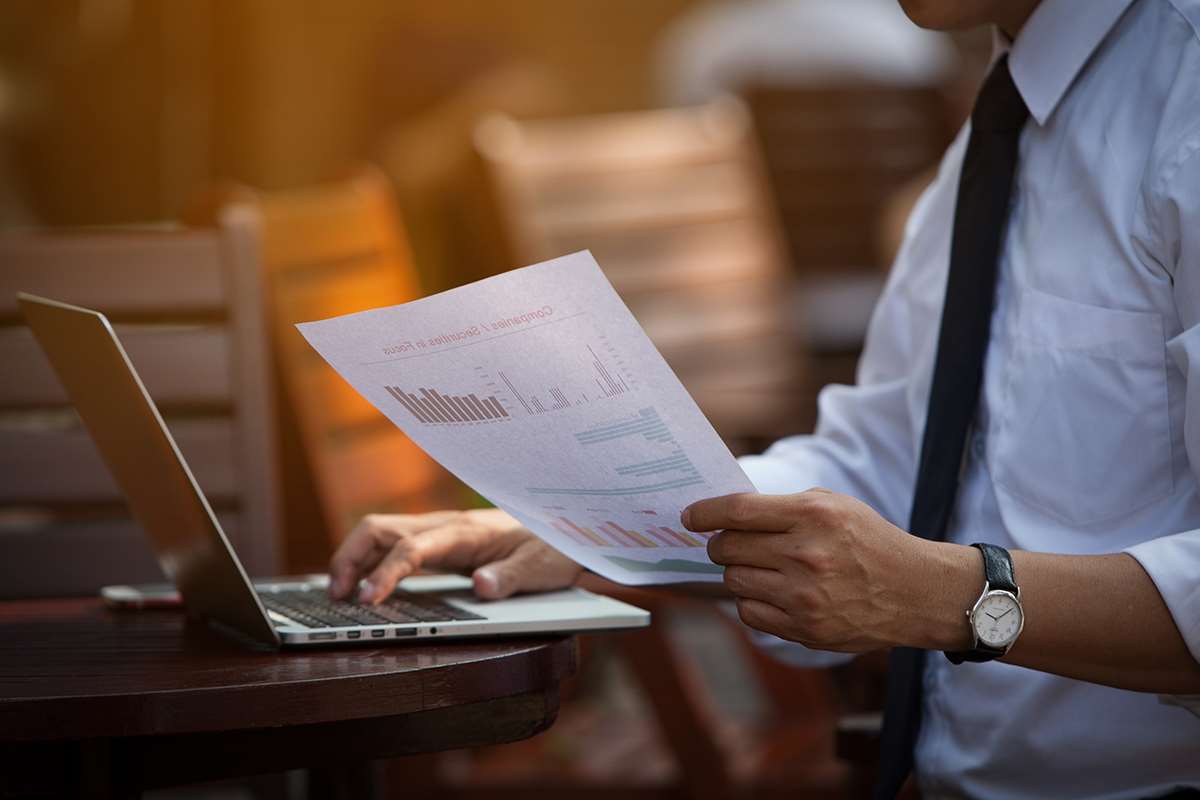
Treasury stock consists of shares that the company has acquired in a buyback. These shares are held in the corporation’s “treasury” rather than in circulation and are therefore excluded from the number of outstanding shares. In the final section of our modeling exercise, we’ll determine our company’s shareholders equity balance for fiscal years ending in 2021 and 2022. From the beginning balance, we’ll add the net income of $40,000 for the current period, and then subtract the $2,500 in dividends distributed to common shareholders. In our modeling exercise, we’ll forecast the shareholders’ equity balance of a hypothetical company for fiscal years 2021 and 2022. Now that we’ve gone over the most frequent line items in the shareholders’ equity section on a balance sheet, we’ll create an example forecast model.

The market capitalization method
- Once you’ve located the number of treasury stocks, write it down for your calculations.
- Finally, outstanding shares are different than authorized shares, or the number of shares that a corporation is legally allowed to issue.
- In particular, when a company issues stock that has a par value, the balance sheet will typically have numbers you can use to calculate issued shares.
- In contrast, outstanding stocks are the ones already issued in the market.
- Shares outstanding are the stock that is held by a company’s shareholders on the open market.
- We have been asked to show how the following transactions will impact the company’s balance sheet and calculate the number of shares outstanding.
A company’s number of outstanding shares is not static and may fluctuate wildly over time. A company’s stock buybacks decrease the book value and total common share count. Stock repurchases occur at current stock prices, which can result in a significant reduction in a company’s book value per common share.

The balance sheet is a financial statement issued by the company that provides a full accounting of the company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder’s equity at a particular moment in time. In other words, the balance sheet is a snapshot of what a company owns, what it owes, and the total amount that has been invested by shareholders. It is worth noting that some companies may choose to list the number of common stock or shares outstanding. And if there is no treasury stock, the number of issued shares will be equal to the number of common stock outstanding. So far, we’ve focused on shares outstanding, whether basic or diluted, at a fixed point in time. In SEC filings, companies will report the total number of shares outstanding on a given day, but in their quarterly and annual figures they must also offer the how to calculate outstanding shares of common stock weighted average shares outstanding.